Bardoxolone
Methyl in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Bardoxolone methyl is an Nrf2 activator currently being investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of
patients
with different forms of chronic kidney disease.
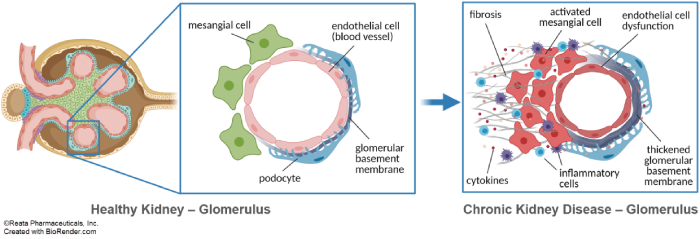
Inflammation—initiated by a variety of pathogenic processes, including
diabetes, systemic hypertension, IgA deposition, and genetic mutations—drives kidney function decline (12).
At the
molecular level, these pathogenic processes induce mitochondrial dysfunction, decrease ATP production, and
promote
production of ROS and pro-inflammatory signaling mediators that initiate and amplify inflammatory pathways
in glomerular
endothelial cells, mesangial cells, and podocytes, while also recruiting activated macrophages and other
inflammatory
effector cells to the renal interstitium. At the physiological level, chronic activation of pro-inflammatory
pathways in
these kidney cells leads to a reduction in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (13-15).
Click to Enlarge
In preclinical models, bardoxolone methyl suppresses inflammatory pathways that contribute to kidney function
loss by increasing Nrf2 activity (1, 7-11). The beneficial activity of bardoxolone methyl and analogs has
been observed in several nonclinical models of CKD, including CKD caused by diabetes, hypertension,
autoimmune disease, nephron loss, and nephrosis (7, 9-11, 16, 17). In these models, bardoxolone methyl and
analogs suppress inflammation and fibrosis (7, 9-11), reduce glomerulosclerosis (10, 11, 17), prevent
tubulointerstitial damage (7, 9-11), and improve kidney function (7, 10, 16, 17).
Follow the links to: